
WHO GMP
WHO GMP, or World Health Organization Good Manufacturing Practices, refers to the guidelines provided by the World Health Organization to ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. These guidelines are designed to minimize the risks involved in any pharmaceutical production that cannot be eliminated through testing the final product.
The World Health Organization Good Manufacturing Practices (WHO GMP) are a set of principles and guidelines developed by the WHO to ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards appropriate for their intended use and as required by the marketing authorization or product specification. WHO GMP aims to safeguard public health by ensuring that all pharmaceutical products are free from contamination and are consistent in their intended use.
Overview of WHO GMP:
Quality Assurance:
WHO GMP encompasses all aspects of production and quality control. It establishes a comprehensive system of quality assurance that integrates Good Clinical Practices (GCP), Good Laboratory Practices (GLP), and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). The core aim is to ensure that products are consistently manufactured to a quality appropriate for their intended use.
Quality Control Environment:
Production must take place under a rigorously controlled environment. Facilities must maintain high levels of cleanliness, and all processes must be clearly defined, validated, and controlled. Any changes to the process must be evaluated for their impact on product quality.
Documentation:
Detailed, clear documentation is essential for GMP. Documentation provides written proof of compliance and operation within the defined standards, and ensures traceability of every aspect of the manufacturing process. This includes batch records, validation documentation, and quality control records.
Personnel:
Competent, well-trained personnel are crucial to GMP compliance. Training programs must be ongoing, and the effectiveness of training should be evaluated regularly. Personnel should understand the principles of GMP that affect them and be provided with the necessary tools to complete their tasks according to these guidelines.
Materials and Production:
Raw materials used in the production of pharmaceuticals must be proven safe, of high quality, and suitable for their intended use. Similarly, all production processes must be clearly defined and controlled, ensuring that each batch of the product is of consistent quality.
Validation and Qualification:
Critical processes are validated to demonstrate consistency and adherence to specifications. Equipment and installations must also undergo qualification and maintenance to ensure they are suitable for their intended purposes.
Risk Management:
WHO GMP involves a proactive approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling potential risks that could impact product quality. This risk management process is integrated throughout the quality management system.
Distribution:
GMP also covers the distribution aspect of pharmaceutical products, ensuring that the quality of medicines is maintained throughout the supply chain, from production to patient.
Complaints and Recalls:
Effective systems must be in place for dealing with complaints about marketed products and for undertaking product recalls when necessary.
Continuous Improvement:
GMP is not static; it requires a continuous improvement approach. Companies must use audit and inspection results, quality reviews, and performance indicators to analyze their quality systems and implement improvements where necessary.
WHO GMP guidelines are not just regulatory requirements but are essential for the production of high-quality pharmaceuticals. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including product recalls, sanctions, and damage to both public health and the manufacturer’s reputation. Therefore, adherence to GMP guidelines is considered a fundamental component of pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and related industries
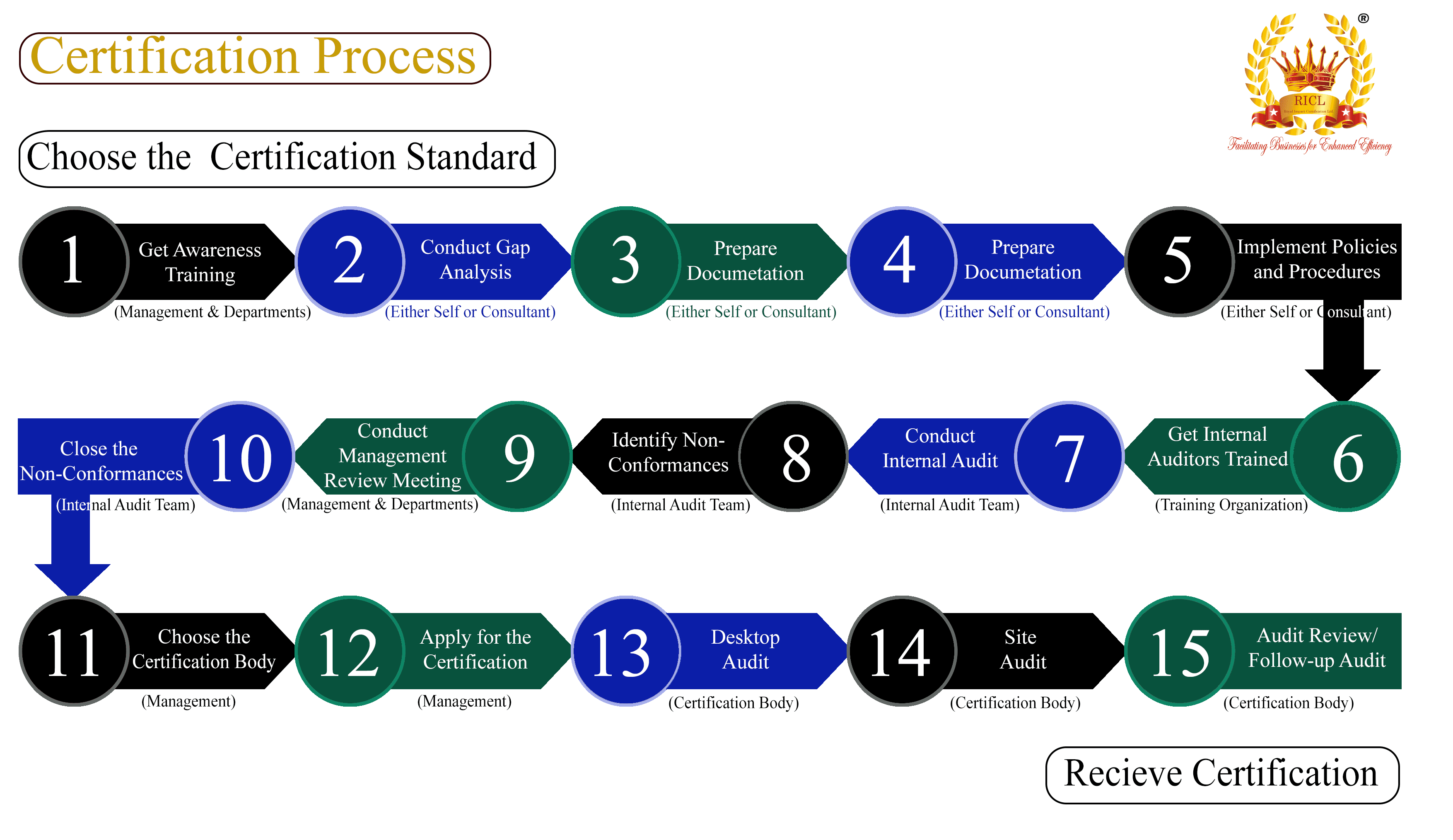
The WHO Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines are relevant across a wide range of industries where the quality and safety of products are of paramount importance. Here are The industries where WHO GMP standards are crucial:
- Pharmaceuticals Manufacturing
- Biotechnology
- Medical Devices
- Blood and Blood Products
- Vaccines
- Diagnostics Products
- Herbal Medicines
- Cosmetics
- Food and Dietary Supplements
- Baby Food Production
- Clinical Trials Supplies
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
- Nutraceuticals
- Veterinary Drugs
- In Vitro Diagnostics
- Gene Therapy Products
- Tissue Engineering
- Stem Cell Products
- Contact Lenses Manufacturing
- Dental Supplies
- Orthopedic Implants
- Surgical Instruments
- Packaging for Pharmaceutical Products
- Chemical Manufacturing
- Biological Products
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- Disinfectants and Antiseptics
- Hormonal Products
- Insulin Production
- Narcotic and Psychoactive Drug Production
- Ophthalmic Solutions
- Parenteral Nutrition Products
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Probiotics Manufacturing
- Respiratory Therapy Products
- Skin Care Products
- Sunscreen Products
- Transdermal Patches
- Wound Care Products
- X-ray Contrast Media
- Essential Oils
- Alcohol and Spirit Production (for medical use)
- Homeopathic Medicines
- Immunoassay Kits
- Implantable Medical Devices
- Inhalation Therapy Products
- Intrauterine Devices
- Liquid Dietary Supplements
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contrast Agents
- Microbiological Culture Media
[sp_easyaccordion id=”10773″]
[formsapp id=”662f63f6c4dd546c9916c3db”]
