
GLP
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) is a set of principles intended to ensure the quality and integrity of non-clinical laboratory studies that are used to support research or marketing permits for products regulated by government agencies. The principles of GLP aim to make certain that the data submitted are a true reflection of the results obtained during the study and can therefore be relied upon when making risk/safety assessments.
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) is a set of principles intended to ensure the quality and integrity of non-clinical laboratory studies that are used to support research or marketing permits for products regulated by government agencies. The principles of GLP aim to make certain that the data submitted are a true reflection of the results obtained during the study and can therefore be relied upon when making risk/safety assessments.
Origin and Purpose
GLP standards were developed by organizations such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) among others. These standards are crucial in non-clinical safety tests of potentially hazardous substances such as pharmaceuticals, industrial chemicals, cosmetic products, veterinary drugs, pesticides, and food additives.
Main Aspects of GLP
Organization and Personnel: Ensuring that there are sufficient and qualified personnel with clear responsibilities.
Facilities: Maintaining facilities that minimize cross-contamination and ensure the orderly conduct of studies.
Equipment, Materials, and Reagents: Equipment must be regularly calibrated and maintained, and materials used must be clearly identified and their quality assured.
Test Systems: The biological, chemical, and physical test systems should be specified and monitored.
Test and Reference Items: Proper storage, handling, and usage of the test and reference items to ensure their integrity.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Detailed, written procedures are required for all processes and activities, which guarantee the quality and consistency of the data.
Performance of the Study: The study must be performed in accordance with the approved study plan, and any deviations should be recorded and justified.
Reporting of Study Results: Reports must fully reflect the methods, results, and observations of the study, and data must be reported in a way that supports good assessment practices.
Storage and Retention of Records and Materials: Proper storage and retention to allow for adequate reconstruction of the conduct of the study.
Importance
GLP is vital for the credibility of research, particularly in the regulatory submission process. Compliance with GLP ensures that the data and reported results are traceable, reproducible, and reliable. It supports regulatory assessment processes by providing a clear and auditable record, thereby protecting public health and the environment.
Through these standards, GLP also aims to facilitate the international acceptance of safety data, which can help reduce the need for duplicative testing, reduce testing costs, and expedite the development process for new substances.
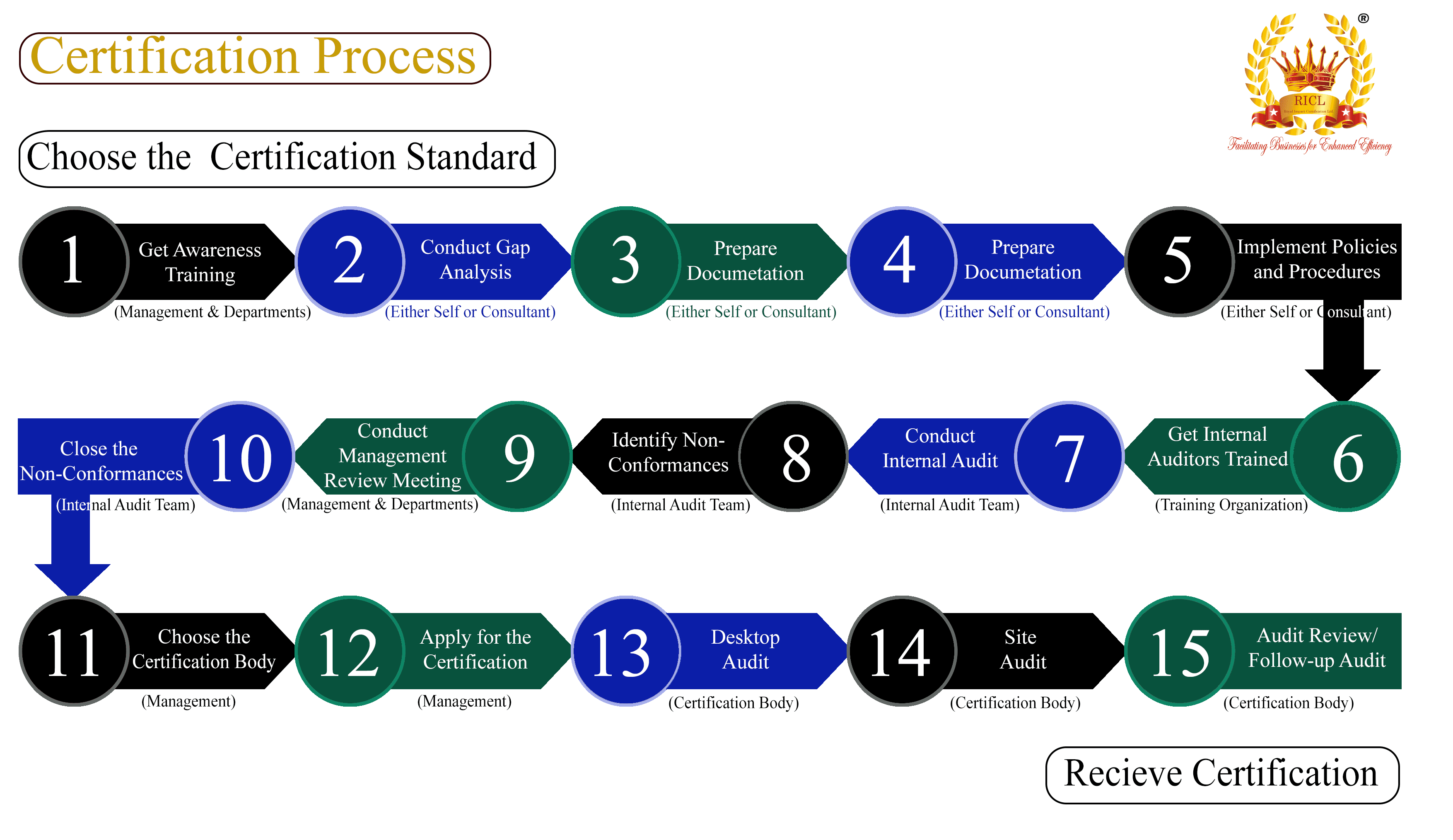
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) standards apply broadly across multiple industries where non-clinical environmental health and safety studies are crucial. Here are the industries that typically require adherence to GLP standards due to the nature of their products and the need for precise and reliable testing results:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Biotechnology
- Medical Devices
- Chemical Manufacturing
- Cosmetics
- Veterinary Medicines
- Agricultural Chemicals (Pesticides)
- Food Additives
- Feed Additives
- Petrochemicals
- Environmental Protection
- Toxicology
- Ecology
- Genetic Engineering
- Industrial Enzymes
- Nutraceuticals
- Packaging Materials
- Paints and Coatings
- Plastics and Polymers
- Cleaning Products
- Textile Industry
- Electronics
- Batteries and Energy Storage
- Automotive Industry
- Aerospace
- Defense
- Public Health
- Water Treatment and Analysis
- Soil and Land Management
- Waste Management
- Renewable Energy (e.g., biofuels)
- Metallurgy
- Mining
- Construction Materials
- Furniture and Wood Products
- Consumer Goods
- Tobacco Products
- Alcohol Products
- Food Packaging
- Printing and Dyeing
- Essential Oils and Aromatics
- Herbal Medicines
- Dietary Supplements
- Pest Control Products
- Home Appliances
- Toys and Children’s Products
- Recreational Equipment
- Sports Equipment
- Office Supplies
- Stationery Products
[sp_easyaccordion id=”10765″]
[formsapp id=”662f63f6c4dd546c9916c3db”]
